ALLO AND GABA
THE BRAIN’S ‘BRAKE SYSTEM’
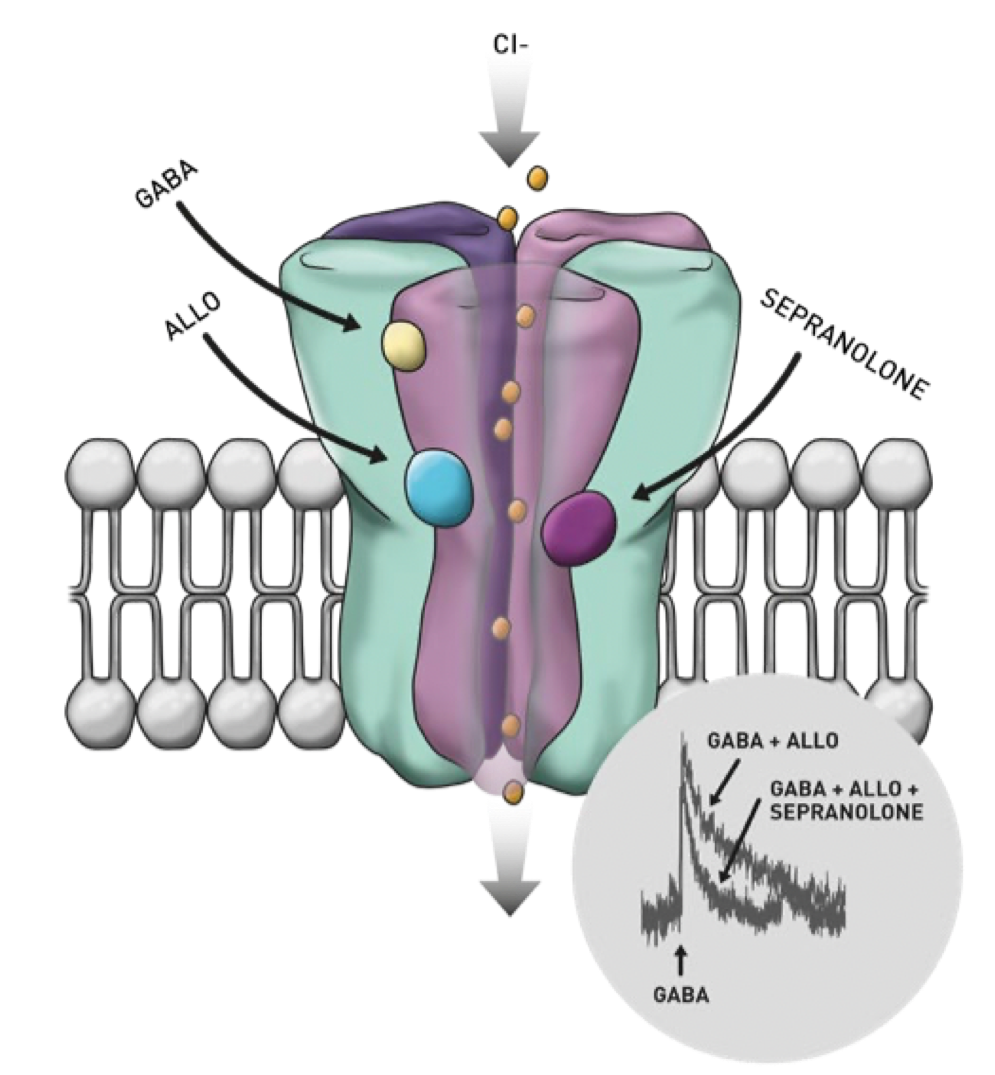
The neurochemical GABA is the brain’s most powerful inhibitory neurotransmitter. It plays a crucial role in inhibiting and reducing stress, fear and anxiety levels and helping us remain in control of our lives. But what keeps GABA in check?
The neurosteroid Allopregnanolone is a potent modulator of GABA, acting on the GABA-A receptor, a chloride channel in the brain that is the major pathway for GABA.
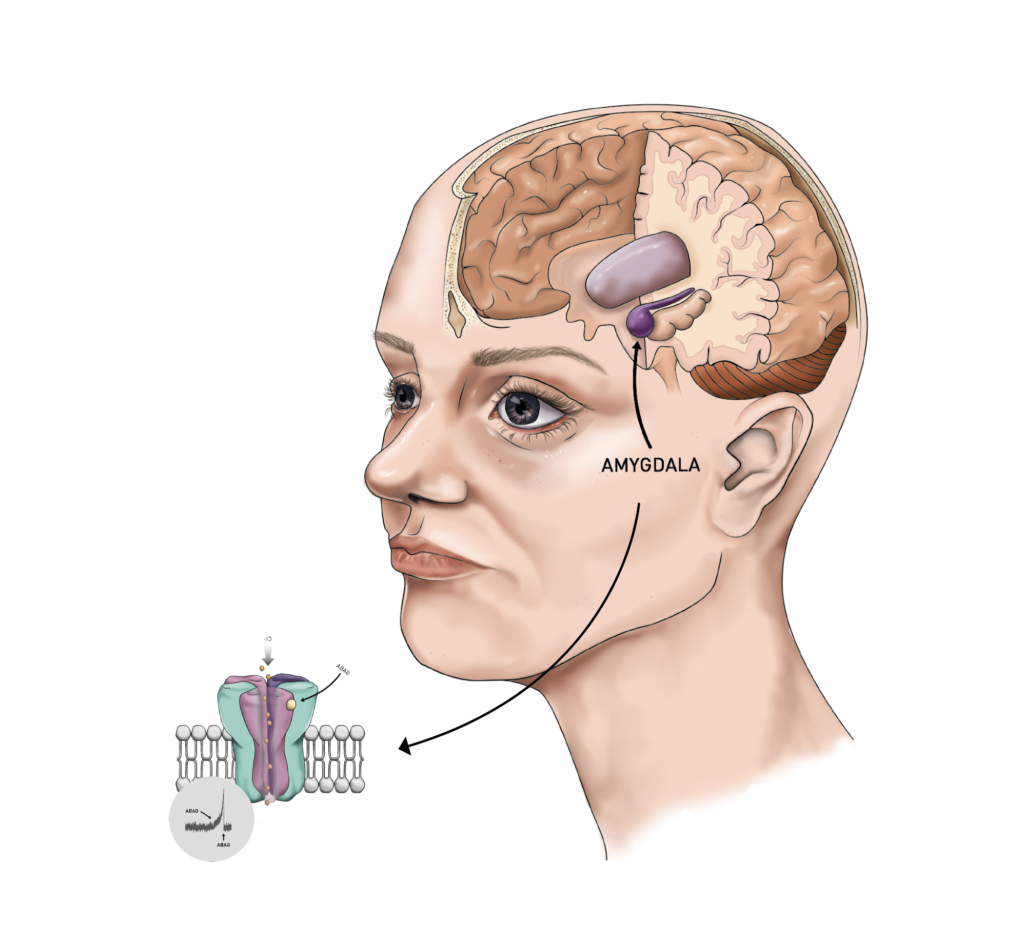
AMYGDALA. The amygdala plays a crucial role in processing emotional responses. Inside the amygdala, neurons use the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) to modulate feelings such as fear, anxiety and agreession. The GABA system is the brain’s primary inhibitory neurotransmitter.
THE ALLO PARADOX
So—if GABA reduces stress, why doesn’t ALLO too? For most of us it does. ALLO plays an important role in making sure GABA reduces our stress, fear and anxiety levels, helping us remain in control of our lives. For a significant minority of people however, ALLO has the exact opposite effect. Instead of calming, reducing or sedating stress, it increases our stress and anxiety levels, producing severe, mood- and personality-altering symptoms and triggering powerful, irresistible compulsion.
The body’s defense for this is Sepranolone, an endogenous neurological compound that regulates and modulates the negative effects of ALLO.